삼킴곤란 단독으로 발현한 피부근염: 증례 보고
Dermatomyositis Presenting with Isolated Dysphagia: A Case Report
Article information
Trans Abstract
We report a case of a 75-year-old woman who was diagnosed with dermatomyositis presenting with isolated dysphagia. There were no obvious cranial nerve deficits with normal motor grade in all the limbs in neurological examinations, but a suspicious rash was observed in the anterior chest. The serum creatine kinase was 306 IU/L, and active myopathic changes in bilateral limb muscles were observed in the electromyography test. Muscle biopsy from vastus lateralis showed perivascular infiltration of mononuclear inflammatory cells, which was compatible with dermatomyositis. She had responded to oral prednisolone and azathioprine.
삼킴곤란이 나타날 수 있는 대표적인 신경근육계질환으로 염증근육병증(inflammatory myopathy)을 포함한 다양한 근육병증, 중증근무력증(myasthenia gravis), 근위축측삭경화증(amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) 등이 있다. 과거에는 특발염증근육병증(idiopathic inflammatory myopathies)을 자가면역 기전에 의한 염증 반응에 따라 다발근염(polymyositis), 피부근염(dermatomyositis), 봉입소체근염(inclusion body myositis) 으로 분류하였으나 최근에는 근조직 병리 소견과 함께 근염특이항체(myositis-specific antibody)가 보고됨에 따라 피부근염, 봉입소체근염, 면역매개괴사근염(immune-mediated necrotizing myositis), 항synthetase증후군, 분류되지 않는 근염으로 분류하기도 한다[1]. 피부근염은 특징적인 병리 소견 및 피부 증상과 근위약이 있을 때 진단할 수 있으며, 피부근염특이항체(dermatomyositis-specific autoantibody)에 따라 6개의 아형으로 나눈다[2].
특발염증근육병증 환자에서 삼킴곤란은 삼킴단계 중 구강 및 인두단계에 관여하는 근육들에 염증 반응이 침범하여 발생하는 것으로 추정된다. 피부근염에서 근위부 근위약이 발생한 이후 혹은 동시에 삼킴곤란이 동반되는 것은 빈번하게 관찰되지만 삼킴곤란이 단독으로 피부근염의 초기 증상으로 발현하는 경우는 드물다. 저자들은 단독 삼킴곤란이 질병의 초기에 주증상으로 나타난 피부근염 환자를 경험하여 이를 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
75세 여자가 2주 전부터 갑자기 발생하여 진행하는 삼킴곤란과 비음으로 방문하였다. 고형식과 유동식에 모두 삼킴곤란이 있었고 증상의 일중변동은 없었다. 환자는 8년 전 갑상선암으로 갑상선전절제술을 시행한 과거력이 있었으며, 갑상선기능저하증으로 씬지로이드를 복용하고 있었다. 그 외 다른 기저질환은 없었으며 씬지로이드 이외에 근력 저하를 유발할 다른 복용약은 없었다. 최근 감염력 혹은 감염을 의심할 수 있는 증상은 없었다. 내원 당시 운동신경계 검사는 목 굽힘 및 척추 기립근 포함하여 사지에서 정상이었으나, 4일 후에는 Medical Research Council 평가에서는 상하지 모두 5등급이었으나 양하지 근위부의 경미한 근력 저하로 가워징후(Gower sign)가 보였고 쪼그리고 앉았다가 일어나지 못했다. 감각신경계, 뇌신경계 검사는 정상이었다. 신체진찰에서는 입궤양, 탈모증, 반구진성발진은 없었으나 양측 어깨, 견갑부와 앞가슴에서 피부발진이 확인되었으며 이는 삼킴곤란이 나타나기 2주 전 알게 되었다고 하였다(Fig. 1). 그 외, 전신의 근육에서 근위축이나 근비대 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 비인두내시경에서 성대의 움직임은 정상이었고 비인두강의 구조적 이상이 확인되지 않았으며, 위내시경검사에서 식도 폐쇄 소견은 확인되지 않았다. 그 외 뇌자기공명영상에서도 증상과 연관된 이상 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 내원하여 시행한 전체혈구계산(complete blood count), 간기능검사, 신기능검사 및 갑상선기능검사는 정상(free T4, 1.34 ng/dL; T3, 0.88 ng/mL; thyroid stimulating hormone, 0.723 μIU/mL)이었다. 혈중 크레아틴키나아제(creatine kinase)는 306 IU/L (정상범위 43-165 IU/L)로 증가되었고, 항핵항체(anti-nuclear antibody, titer 1:160), 항DNA항체(anti-DNA antibody) 및 루프스항응고항체(lupus anticoagulant)가 양성이었다. 그 외 C3는 77 mg/dL (정상범위 86-160 mg/dL), C4는 19 mg/dL (정상범위 17-45 mg/dL)로 C3의 감소가 확인되었다. 종양표지자와 부종양성 항체검사는 정상이었고, 양전자방출단층촬영(positron emission tomography-computed tomography)에서 종양성 병변을 시사하는 이상 소견은 관찰되지 않았다. 신경전도검사는 정상이었고, 근전도검사에서는 우측 어깨세모근(deltoid muscle), 위팔두갈래근(biceps brachii muscle), 첫번째 등쪽뼈사이근(first dorsal interosseous), 엉덩허리근(iliopsoas muscle), 가쪽넓은근(vastus lateralis muscle) 및 앞정강근(tibialis anterior)에서 삽입활동전위(insertional activity)가 증가하였으며, 섬유자발전위(fibrillation potential)와 양성예파(positive sharp wave)가 관찰되었다. 운동단위활동전위(motor unit action potential, MUAP) 분석에서는 다상활동전위(polyphasic MUAP)와 조기동원(early recruitment) 이 관찰되어 근육병증을 의심할 수 있었다. 반복 신경자극검사는 정상이었다. 대퇴부 근육의 자기공명영상에서 중간넓은근, 안쪽넓은근, 가쪽넓은근에서 비특이적 근육염이 의심되는 소견이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2). 좌측 가쪽넓은근에서 근육조직검사를 하였고, 혈관주위 단핵구 침윤(perivascular infiltration of mononuclear inflammatory cells)이 관찰되었다(Fig. 3A). 추가로 앞가슴의 피부 병변에서 피부조직검사를 시행하였고, 기저각질세포(basal keratinocyte)의 공포성 변화(vacuolar change)가 관찰되었으며 이는 피부근염에서 관찰될 수 있는 피부 병리 소견이었다(Fig. 3B). 경구 프레드 니솔론과 아자치오프린 투여 10일 후부터 양하지 근위부 근력이 호전되어 쪼그리고 앉았다가 일어나는 것이 가능하였다. 치료 2개월 후 삼킴곤란도 호전되었으며 혈중 크레아틴키나아제 수치도 정상화되었다(creatine kinase 25 IU/L). 환자의 삼킴곤란의 정도를 평가하기 위해 비디오투시연하 검사를 치료 1개월과 2개월 후 각각 시행하였다. 첫번째 검사에서는 모든 성상의 식이에서 기도침투 소견이 관찰되었고 인두부의 추진운동이 되지 않아 후두부에 잔여물이 남아있는 소견이었으나, 2개월 후의 검사에서는 인두부에 약간의 잔여물이 남았으나 기도흡인이 관찰되지 않아 연식으로 경구 식이를 시작할 수 있었다.
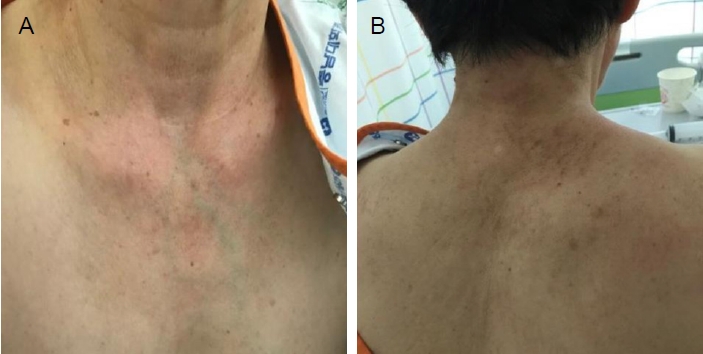
A shawl sign featuring an erythematous rash was observed across (A) the upper chest and neck and (B) the shoulder and scapular region in the patient.
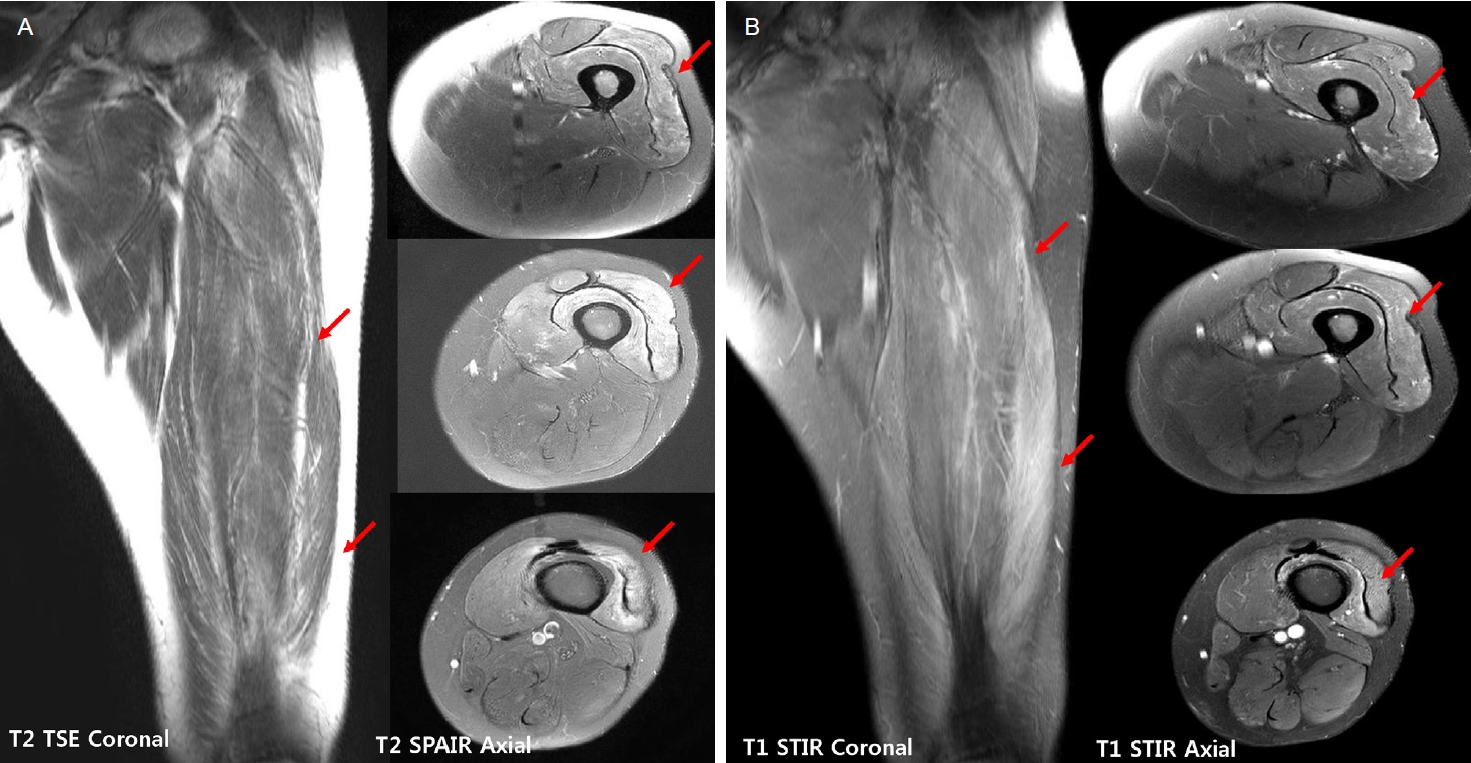
The patient’s proximal thigh coronal and axial view on magnetic resonance imaging. (A) The T2 turbo-spine-echo (TSE) coronal and T2 spectral adiabatic inversion recovery (SPAIR) axial images show edematous changes of muscle fascia in the left vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius muscles (red arrows) and (B) the fat-suppressed T1 short tau inversion recovery (STIR) image with gadolinium enhancement reveals enhancement in the left vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius muscles (red arrows). The findings are suggestive of inflammatory myositis.
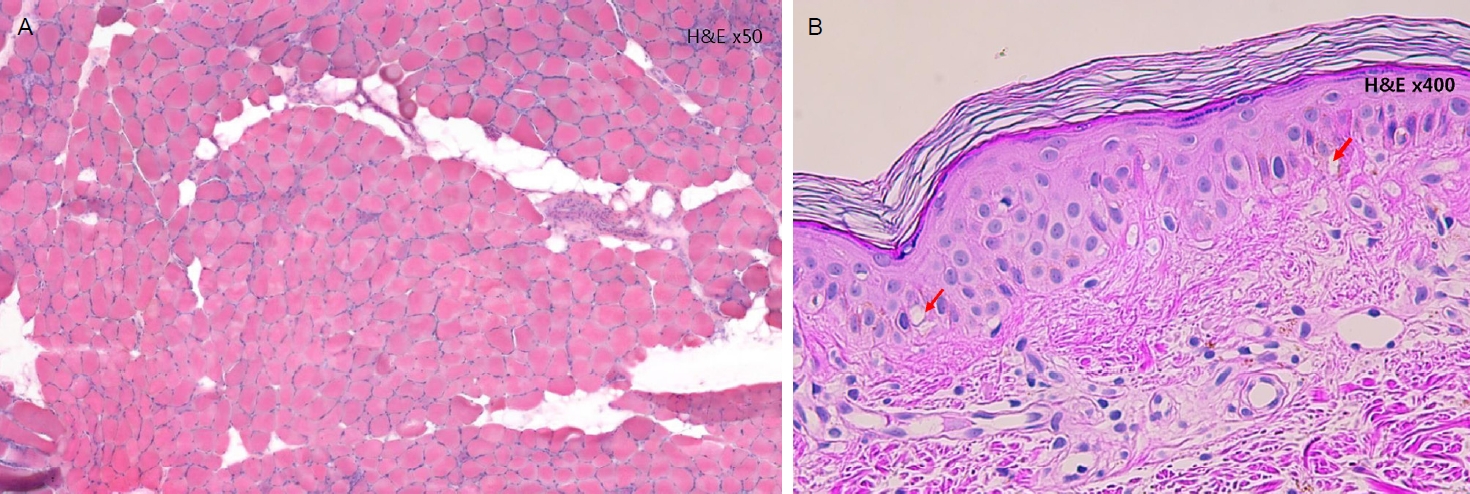
The histopathology of the left vastus lateralis muscle and skin lesion of the anterior chest. (A) The Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining (×50) revealed perivascular infiltration of mononuclear inflammatory cells. (B) The histopathology of the skin showed superficial perivascular dermatitis and vacuolar change of the basal keratinocytes (H&E, ×400).
고 찰
피부근염은 비교적 드물게 발생하는 신경근육계질환으로 자가면역성 염증 반응이 골격근을 침범하여 발생하는 대표적인 염증근육병증이다. 피부근염에서는 일반적으로 통증을 동반하지 않는 근위부의 근 위약과 함께 피부 병변이 관찰되는데 대표적으로 동반될 수 있는 피부 병변으로는 눈꺼풀에 발생하는 연한 보라색의 헬리오트롭 발진(heliotrophic rash), 손가락 관절 및 팔꿈치, 무릎, 발목의 폄쪽에 발생하는 분홍색에서 보랏빛 색을 띄는 고트론 구진(Gottron’s papule), 어깨와 견갑부, 앞가슴에 나타나는 발진인 어깨걸이 징후(shawl sign) 등이 있다[3]. 피부근염에서 피부 병변이 관찰되지만 근육침범이 없는 경우(clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis)는 근염으로 진단하기에 어려움이 있다. 반대로 사지 근위부의 위약이 있지만 피부 병변이 없는 경우(dermatomyositis sine dermatitis)에도 임상적으로 다발근염과 구분하기 어렵다. 피부근염의 확정 진단은 2003년 제시된 European Neuromuscular Centre-idiopathic inflammatory myopathies 분류법에 따르면 아급성 또는 서서히 발생하는 대칭적 지대형(limb girdle-type) 근 위약이 특징적인 피부 병변과 동반되면서 근조직병리검사에서 다발주변위축이 관찰될 때 가능하다. 근육자기공명영상에서 근막에 부종이 보이는 것도 피부근염의 특징적인 소견이다[2,4]. 최근 피부근염에서 발견되는 근염특이항체에 따라 피부근염을 항transcription intermediary factor 1-γ피부근염, 항nuclear matrix protein 2피부근염, 항Mi-2피부근염, 항melanoma differentiation associated gene 5피부근염, 항small ubiquitine-like modifier activating enzyme피부근염과 항체음성 피부근염으로 분류하기도 한다[1]. 본 증례는 사지 근위부 근력의 위약은 없었지만 삼킴곤란, 어깨 및 견갑부와 앞가슴에서 관찰되었던 어깨걸이 징후, 근육자기공명영상에서 근막 부종, 피부근염에 합당한 근조직병리검사 결과로 피부근염으로 진단할 수 있었다. 본 환자의 경우 루푸스항응고항체와 항DNA항체에서 양성 및 C3의 감소로 전신홍반루푸스의 가능성에 대한 고려도 필요하였으나 구강궤양, 반구진성 발진, 탈모증과 같은 다른 임상 증상이 없었고, 2019년 제시된 The European League Against Rheumatism and the American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus에 따르면 전신홍반루푸스보다 더 타당한 진단이 있을 경우 항체검사 양성 소견에 의미를 두지 않기에 전신홍반루푸스는 진단에서 배제하였다[5]. 근염 특이항체검사는 시행하지 못해 피부근염의 아형을 구별하기는 어려웠지만, 앞서 기술한 소견들과 혈청내 근육효소의 증가, 근육병에 합당한 근전도검사 결과를 바탕으로 조기에 피부근염으로 진단하여 치료가 가능하였다.
특발염증근육병증 환자에서 비인두삼킴곤란의 발생은 약 10-73%까지 다양하게 보고되고 있다[6,7]. 특발염증근육병증 중 봉입소체근염에서 삼킴곤란의 빈도가 가장 높으며, 봉입소체근염을 제외한 다발근염과 피부근염 환자에서 발생하는 비인두삼킴곤란의 빈도는 약 12-54%로 알려져 있다[8]. 피부근염 환자에서 삼킴곤란이 사지의 위약과 동시에 발생하거나 사지의 위약이 발생한 이후 나타나는 경우는 비교적 빈번하나 질병의 초기 증상으로써 사지의 근위약 없이 삼킴곤란 단독으로 발현하는 경우는 매우 드물다. Elmdaah 등[9]의 연구에서 보고된 58세 환자의 증례에서는 주증상이 삼킴곤란이었지만, 양측 상지에서 경미한 근위부근 위약이 관찰되었고, 안면부와 양측 팔꿈치, 손관절부위에 특징적인 피부 병변이 동반되었으며 최종적으로 피부근 염으로 진단되었다. 국내에서도 삼킴곤란과 관련한 피부근염의 증례보고가 있었다. Kwon 등[10]의 연구에서 보고된 53세 환자는 단독으로 삼킴곤란이 악화되었으나 삼킴곤란 발생 2개월 전 전신위약과 근육통이 선행하였고, 당시 시행한 진찰에서 사지 근위부에서 근력저하가 관찰되었으며, 특징적인 피부 병변 및 혈청 크레아틴키아나제의 상승, 근조직병리검사 소견으로 피부근염으로 진단되었던 환자였다. 하지만 본 증례의 환자와 같이 피부근염의 첫 증상으로 사지 위약 없이 삼킴곤란이 단독으로 발현한 보고는 없었다.
특발염증근육병증 환자의 약물 치료는 무작위 배정 임상 시험이 이루어진 적은 없으나 임상적으로 글루코코르티코이드의 투여가 선호된다. 그 외 다른 면역억제제인 아자치오프린, 메토트렉세이트를 단독으로 사용하기도 하며, 이들의 병용 투여로 스테로이드 제제의 용량을 감량하는 효과를 얻기도 한다. 글루코코르티코이드에 반응이 적은 경우에는 정맥내 면역글로불린, 사이클로포스파마이드 투여 또는 혈장교환술도 시행해 볼 수 있다[11]. 피부근염 환자에서 삼킴 곤란이 동반되는 경우는 삼킴곤란을 동반하지 않은 환자들에 비하여 스테로이드 치료에 반응이 적은 것으로 알려져 있다[12]. 따라서 약물 치료와 함께 연하 재활 치료를 병행하는 등 다학제적인 관점에서 접근하는 것이 환자의 예후에 도움이 된다.
단독 삼킴곤란으로 발현할 수 있는 신경근육계질환은 다양하며, 그중 드물지만 피부근염에서도 단독 삼킴곤란으로 발현이 가능하다. 비전형적인 증상으로 시작하는 피부근염 환자에서 진단에 단서를 얻기 위해서는 신경계진찰 외에도 면밀한 신체진찰로 피부 상태를 살피는 것이 중요하고, 사지 위약이 없어도 근전도검사가 진단에 도움이 될 수 있어 이에 대하여 증례를 보고하는 바이다.